Problem 1.15:
Solution:
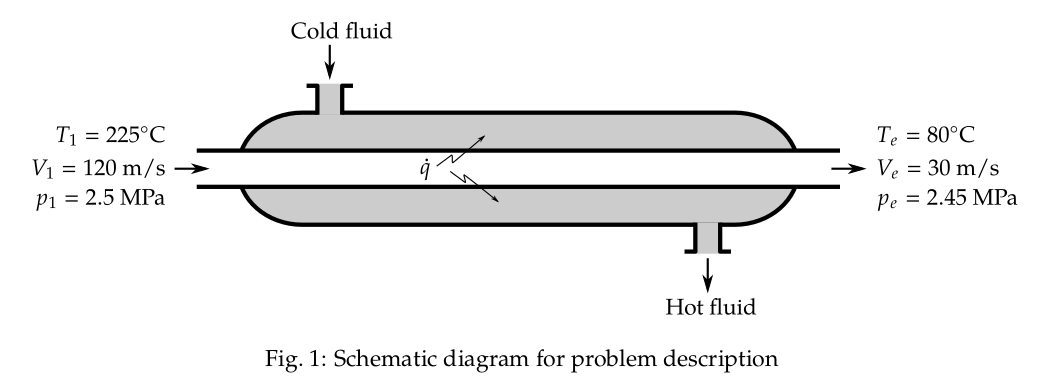
Given:
\( V_{1} = 120\,\text{m/s} \),
\( T_{1} = 225^{\circ}\,\text{C} = 498\,\text{K} \),
\( p_{1} = 2.5\,\text{MPa} \),
\( V_{e} = 30\,\text{m/s} \),
\( T_{e} = 80^{\circ}\,\text{C} = 353\,\text{K} \),
\( p_{e} = 2.45\,\text{MPa} \).
To calculate: \( \dot{q}/\dot{m} = ? \), \( \rho_{1} = ? \), \( \rho_{e} = ? \).
The schematic diagram of the problem description is shown in Fig. 1.
Applying the conservation of energy,
$$ \text{Rate of energy at inlet} + \text{Rate of heat addition} = \text{Rate of energy at exit} $$ $$ c_{p}T_{1}+\frac{V_{1}^{2}}{2}+\frac{\dot{q}}{\dot{m}}=c_{p}T_{e}+\frac{V_{e}^{2}}{2} $$Taking the heat capacity of air at constant pressure, \( c_{p}=1005\,\text{J/kg-K} \),
$$ 1005 \times 498 + \frac{120^{2}}{2} + \frac{\dot{q}}{\dot{m}} = 1005 \times 353 + \frac{30^{2}}{2} $$ Which can be solved for heat flow rate to be, $$ \frac{\dot{q}}{\dot{m}} = 1005 \times 353 + \frac{30^{2}}{2} - 1005 \times 498 - \frac{120^{2}}{2} = -152475\ . $$The negative sign indicates that the heat is removed. The heat removed per kilogram of air flowing through the heat exchanger,
$$ \boxed{\frac{\dot{q}}{\dot{m}}=152475\,\text{J/kg}}\ . $$--- Ad ---
---
The density at the inlet and exit can be calculated using the ideal gas equation.
$$ \rho_{1}=\frac{p_{1}}{R\,T_{1}}=\frac{2.5\times10^{6}}{287\times498} $$ $$ \boxed{\rho_{1}=17.49\,\text{kg/m}^{3}}\ . $$ $$ \rho_{e} = \frac{p_{e}}{R\,T_{e}} = \frac{2.45 \times 10^{6}}{287 \times 353} $$ $$ \boxed{\rho_{e}=24.18\,\text{kg/m}^{3}}\ . $$