Problem 1.13:
Solution:
Given:
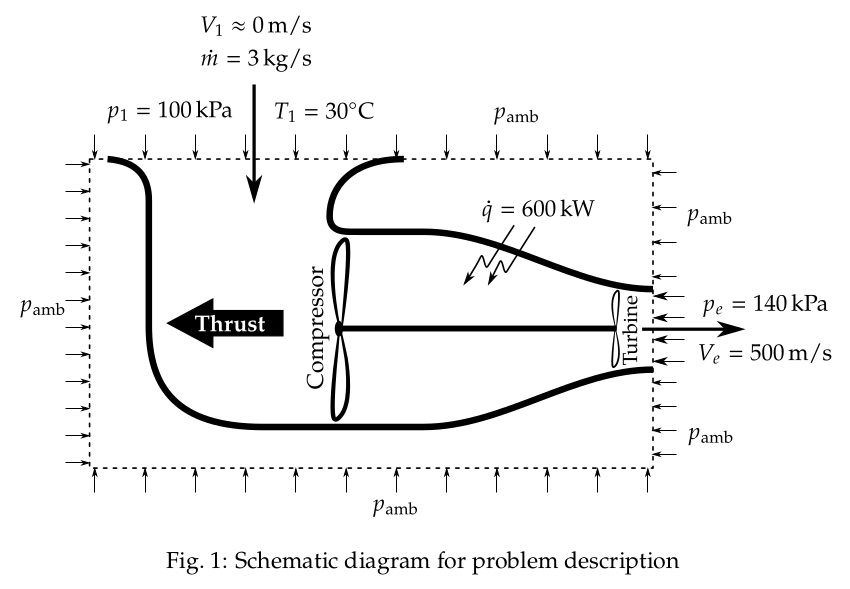
Air is drawn vertically, \( \dot{m}=3\,\text{kg/s} \),
\( V_{1}\approx0\,\text{m/s} \),
\( p_{\text{amb}}=p_{0}=100\,\text{kPa} \),
\( T_{\text{amb}}=T_{0}=30^{\circ}\,\text{C}=303\,\text{K} \).
Air is compressed and heated and discharged horizontally,
\( V_{e}=500\,\text{m/s} \),
\( p_{e}=140\,\text{kPa} \),
\( \dot{q}=600\,\text{kW} \).
To calculate: \( A_{e}=? \), \( \text{Thrust}=? \).
The schematic diagram of the problem description is shown in Fig. 1.
Applying the conservation of energy through the system,
$$ \begin{aligned} \text{Rate of energy entering}\ &+\ \text{Rate of heat addition} \\ &=\text{Rate of energy leaving}\ +\ \text{Work done by the system} \end{aligned} $$ $$ \dot{m}\,c_{p}T_{0}+\dot{q}=\dot{m}\,c_{p}T_{e}+\dot{m}\,\frac{V_{e}^{2}}{2}+W $$ $$ 3\times1005\times303+600\times10^{3}=3\times1005\times T_{e}+3\times\frac{500^{2}}{2}+0 $$ $$ T_{e}=\frac{3\times1005\times303+600\times10^{3}-3\times\frac{500^{2}}{2}}{3\times1005}=377.627\,\text{K}\ . $$--- Ad ---
---
The density at the exit can be calculated using the ideal gas equation,
$$ \rho_{e}=\frac{p_{e}}{R\,T_{e}}=\frac{140\times10^{3}}{287\times377.6}=1.29176\,\text{kg/m}^{3} $$Applying the conservation of mass equation,
$$ A_{e}=\frac{\dot{m}}{\rho_{e}V_{e}}=\frac{3}{1.29176\times 500} $$ $$ \boxed{A_{e}=0.0046448\,\text{m}^{2}}\ . $$Applying the conservation of horizontal momentum,
$$ \text{Thrust}=\dot{m}_{e}V_{e}+\left(p_{e}-p_{\text{amb}}\right)A_{e} $$ $$ \text{Thrust}=3\times500+\left(140\times10^{3}-100\times10^{3}\right)\times0.0046448 $$ $$ \boxed{\text{Thrust}=1685.79\,\text{N}}\ . $$