Problem 1.10:
A rocket used to study the atmosphere has a fuel consumption rate of 120 kg/s and a
nozzle discharge velocity of 2300 m/s. The pressure on the nozzle discharge plane
is 90 kPa. Find the thrust developed when the rocket is launched at sea level.
The nozzle exit plane diameter is 0.3 m.
Solution:
Given:
\( \dot{m}_{fuel}=120\,\text{kg/s} \),
\( V_{e}=2300\,\text{m/s} \),
\( p_{e}=90\,\text{kPa} \),
\( D_{e}=⌀0.3\,\text{m} \).
To calculate: Thrust at sea level.
The schematic diagram of the problem description is shown in Fig. 1.
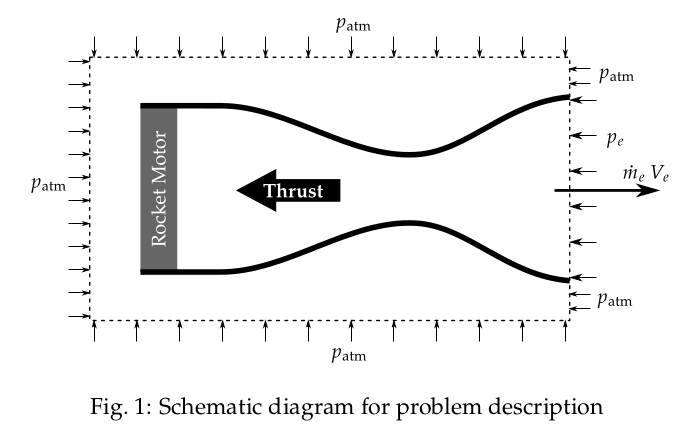
Assuming the atmospheric pressure at sea level as \( p_{\text{atm}}=1\,\text{atm}=101325\,\text{Pa} \).
Assuming that the oxidizer is mixed with the fuel, \( \dot{m}_{e}=\dot{m}_{fuel}=120\,\text{kg/s} \).
Applying the conservation of momentum on the control-volume around the rocket,
$$ \begin{aligned} \text{Thrust} =&\ \text{rate of momentum exiting }-\text{ rate of momentum entering}\\ &\ +\text{ pressure force at exit }-\text{ pressure force at inlet}\\ \\ \text{Thrust} =&\ \dot{m}_{e}V_{e}-0+\left(p_{e}-p_{\text{atm}}\right)A_{\text{exit}}\\ \\ \text{Thrust} =&\ 120\times2300-0+\left(90\times10^{3}-101325\right)\times\frac{\pi}{4}\times0.3^{2} \end{aligned} $$ $$ \boxed{\text{Thrust at sea level}=275199.483\,\text{N}}\ . $$